TRENDING
The Incredible Story of Elon Musk
Published
3 years agoon
Elon Musk has quickly become one of the most polarizing and influential figures of the last decade, and everyone around the world knows it. From his technological innovations, to his amassed wealth, people are constantly trying to figure out just what the engineer and business guru might do next.

But that’s tougher to predict without knowing the origins of Elon Musk, how he began and funded his companies, and what he plans to do with his fortune in the future. Musk’s past is one of grit and fortune, but also a calculated timeline of perseverance and smart business practices. If you want to learn how Elon created the empires of Tesla, SpaceX, and what he’ll do beyond, dive in!
Born June 28, 1971
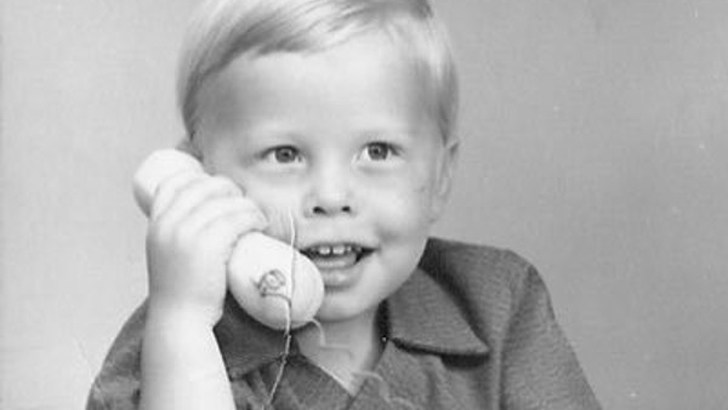

Elon Musk was born in Pretoria, South Africa to a South African father and Canadian mother.
His mom was a model and dietician, while his father worked as an electromechanical engineer and property manager. When he was young, they removed his adenoids assuming he was deaf, but his mom later came to the conclusion he must’ve been thinking “in another world.”
Parents’ Divorce
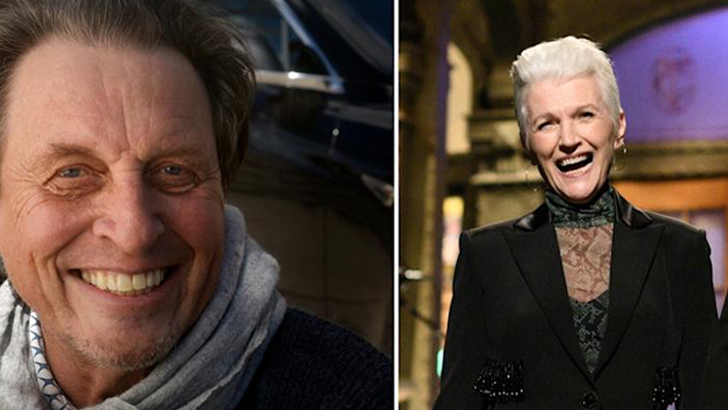

When Musk was just 9 years old, his parents split, resulting in him living with his father up until he was 17. Musk has publicly stated that he regretted this decision, calling his father a “terrible human being,” saying that he’s done all the bad things one could do. During this time, he continued to live in and around Pretoria.
Self-Taught Programmer

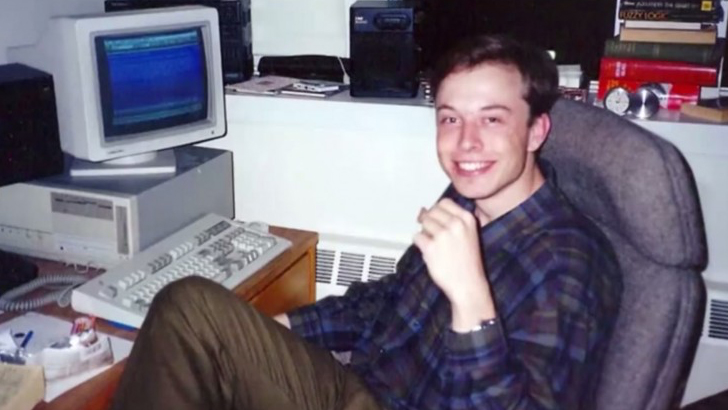
At the mere age of 10, Musk was introduced to the Commodore Vic-20, marking his first interaction with a computing machine where he would later begin to learn programming on his own. Though he was inherently smart, he often was bullied as a child, and he was once hospitalized after being thrown down a flight of stairs by another group of boys.
Blastar

By age 12, Elon Musk had already developed his own video game using BASIC-based code, and he was able to sell it to a magazine called PC and Office Technology for $500. The game is just a simpler version of Space Invaders or Asteroid, but was surely impressive for a child his age at the time.
Move to Canada

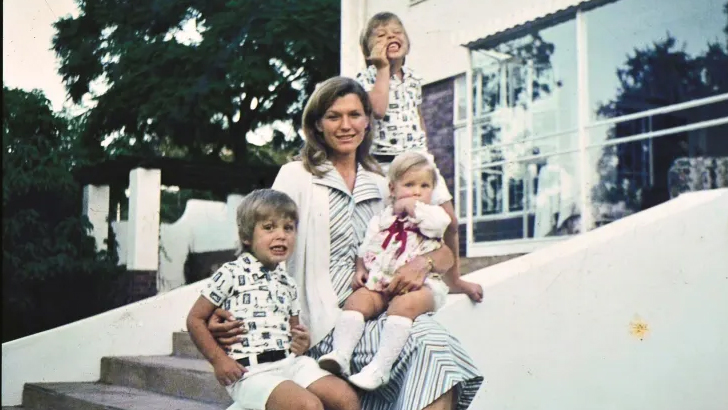
After deciding he liked the economic opportunities in the United States much better, he took an abject stance on apartheid and involuntary military service in the South African Army and Musk obtained a Canadian visa by way of his mother. He made the transition in 1989 after spending 5 months at Pretoria University awaiting his approval.
Queens University
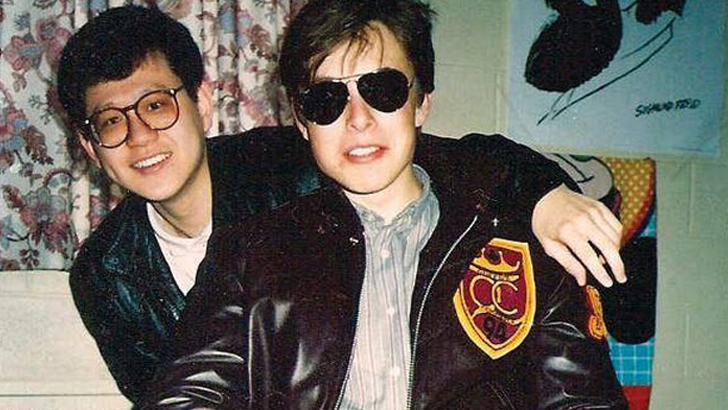

Elon moved to Canada in June of 1989 and stayed with his second cousin, who lived in Saskatchewan. For work, Musk spent his time working odd jobs around the lumber mill and farm. He was awaiting enrollment to Queen’s University in Kingston, Ontario, where he would spend the next two years.
Transfer to Penn
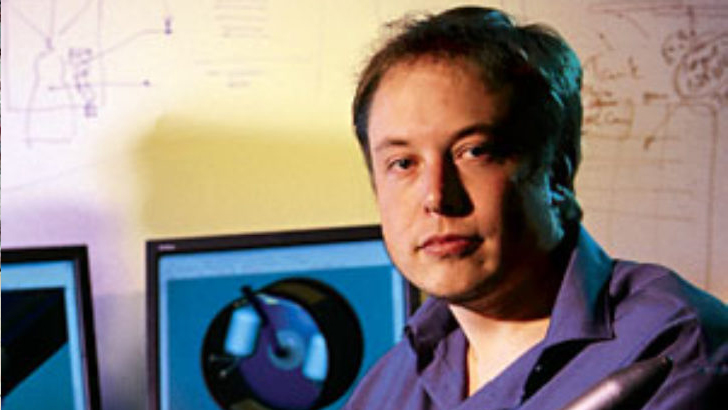

Elon Musk transferred to the University of Pennsylvania in 1992, where he would spend his next 5 years earning two separate degrees. One Bachelor of Arts degree in physics, and one Bachelor of Science degree in economics from the Wharton School. He would later graduate in 1997.
Zip2
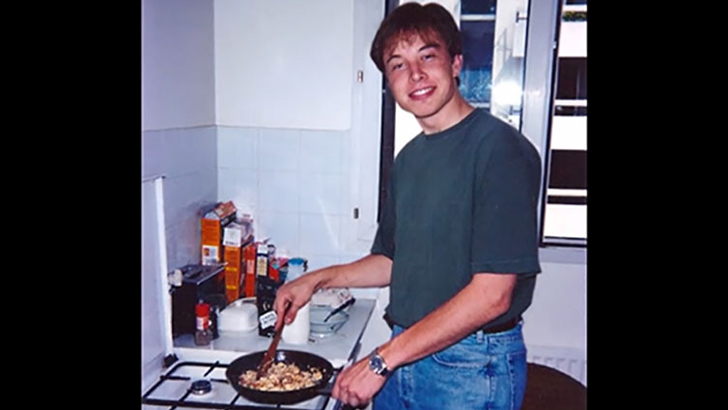

In 1995, Elon and his brother Kimbal founded the company Zip2, which compiled an internet city guide consisting of things like yellow pages, maps, and other newspaper publishings that had local relevance. It was funded by angel investors, and the Musk brothers shared one computer, with Elon claiming to have slept on the couch at the office and shower at the YMCA.
Failed CEO Bid & Buyout

Running Zip2 surely primed Elon to disappointment early in his entrepreneurial career, despite him putting in effort coding nightly 7 days a week and keeping the site up during the day. While Zip2 gained the trust of The New York Times and The Chicago Tribune, Elon’s attempt to move into the role of CEO was squashed by the board, and Compaq would buy the company for $307 million in 1999, leaving Musk with a $22 million payout equating to his 7% of ownership.
X.com

In 1999, using his payout from Zip2, Musk founded an email payment company called X.com, which offered financial services as one of the first federally insured online banks. Though it immediately experienced solid customer sign-ups, investors ousted Musk for his inexperience, and the company would later merge with Confinity, whose company PayPal outperformed X.com.
PayPal CEO

After the merger, Musk briefly served as the CEO of PayPal, however, his software preferences caused a rift in the company. He preferred Microsoft to Unix, which caused founder Peter Thiel to resign. After this, Musk’s business model never came into fruition, and he was once again ousted in replacement for Thiel in 2000.
First Marriage
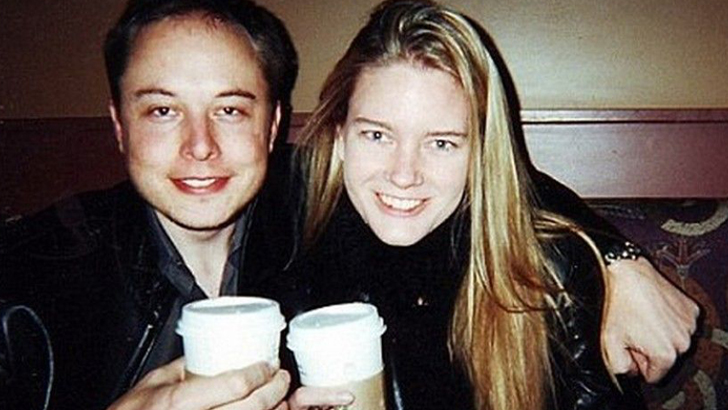

Elon Musk married his first wife Justine Wilson in 2000, whom he met at Queens University where they both attended school. Wilson was an author originally from Canada herself. However, in 2000, Musk traveled to South Africa and caught malaria, almost killing him. After their first child died in 2002 after only 10 weeks due to SIDS, the two used IVF to have their next 5 sons, a set of twins, and a set of triplets. The couple divorced in 2008 and have shared custody of the children.
Mars Society & Missiles
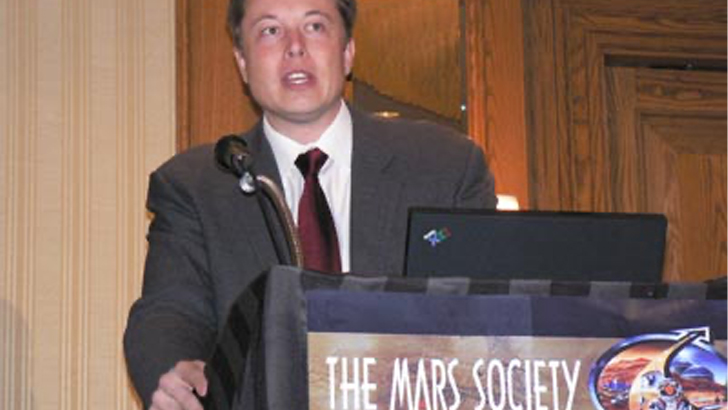

Elon became interested in the Mars Society, a non-profit promoting the importance of the colonization of the planet, and he first became interested in growing plants there in 2001. He would travel to Moscow later that year to try and acquire Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles which he could use to send materials to space. However, he came back empty-handed.
SpaceX Origins
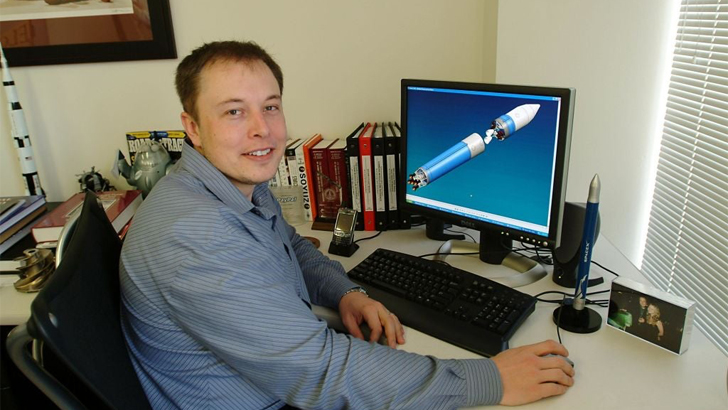

After PayPal was acquired by eBay in 2002, Musk received a payout of nearly $176 million. This worked perfectly for his new plan, as he decided to found Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX as we know it today, with the intention of building his own affordable rockets. At that moment, Elon went from literally being spat at by a Russian rocket designer to found his own company for $100 million in May of 2002.
Tesla Beginnings
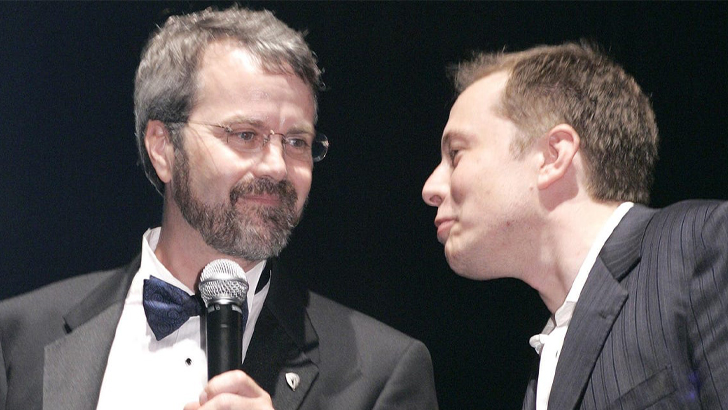

The early days of Tesla started through their incorporation in 2003, in which Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning financed the company during its initial Series A funding period. However, Musk would come along in 2004, making a new majority investment of $6.5 million and becoming the chairman of the board. He served actively initially, but not in business relations.
Elon’s Sons
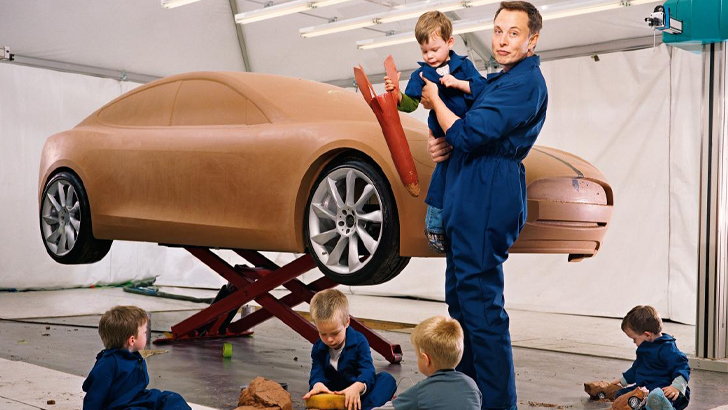

It was around this time that Musk and his then-wife Justine had their sets of sons through in-vitro fertilization. In 2004 the couple had twins, Xavier and Griffin, and in 2006, they welcomed triplets, Kai, Saxon, and Damian. Though the couple share custody of the five boys, not much is known about their future although they’re all rapidly approaching adulthood.
SolarCity

Musk wasn’t done with his business endeavors, however, as he also came up with the original idea and financial backing for a company co-founded by his cousins, Lundon and Peter Rive. That company was SolarCity, who specialized in solar-powered generators and products for both commercial and residential buildings. Later, this would turn out to be a huge investment.
First SpaceX Launch
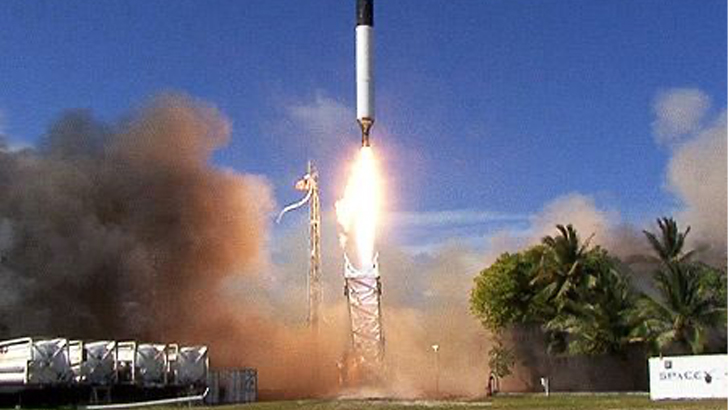

Meanwhile, Musk was still trying to literally get his rockets off the ground, and although a failed attempt to reach orbit occurred when the very first Falcon 1 launched in 2006, NASA gave SpaceX its first contracts to later take part in helping NASA ship cargo and even potentially astronauts to the International Space Station. But this didn’t come without immense struggle..
Failed Launches

Despite receiving the contracts, Musk and SpaceX continued to struggle getting the Falcon series of rockets to launch properly. This reportedly caused the CEO and Head Engineer an abundance of stress, with him being quoted as saying he was “waking from nightmares, screaming and in physical pain.” No one was saying it would be easy.
Tesla Promotion
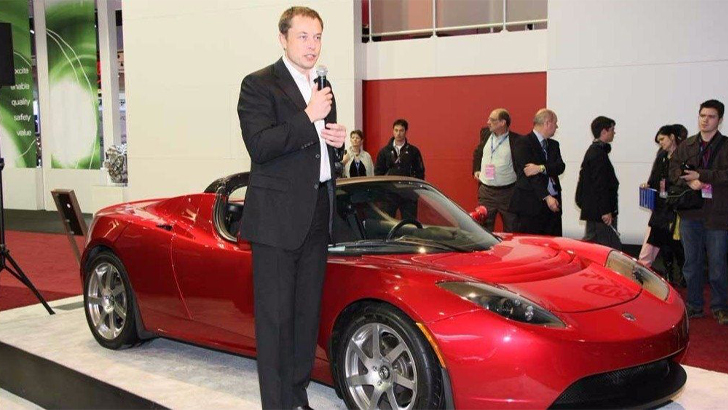

After Eberhard, one of the initial investors in Tesla, was ousted following conflicts and the financial crisis at the time, Musk was ushered in as the new CEO, as well as product architect in 2008. A lawsuit in 2009 would later etch him as the company’s co-founder, with Tarpenning and two others. Musk’s credibility was certainly enhanced due to his oversight of the 2008 Roadster.
Falcon 1
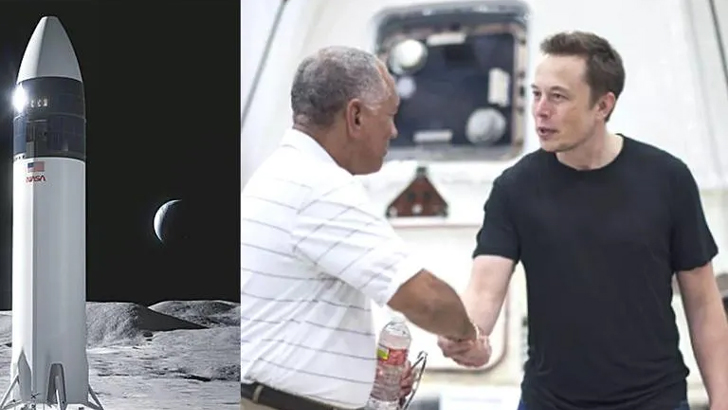

Despite the failed attempts previously, SpaceX was finally able to get their Falcon 1 rocket into orbit in 2008, earning it the honor of being the first liquid-fueled and privately-owned rocket to ever do so. Because of these successes, the Commercial Resupply Services program from NASA granted them a $1.6 billion contract to take over the retiring space shuttle, earning them 12 future missions to the ISS.
Talulah Riley
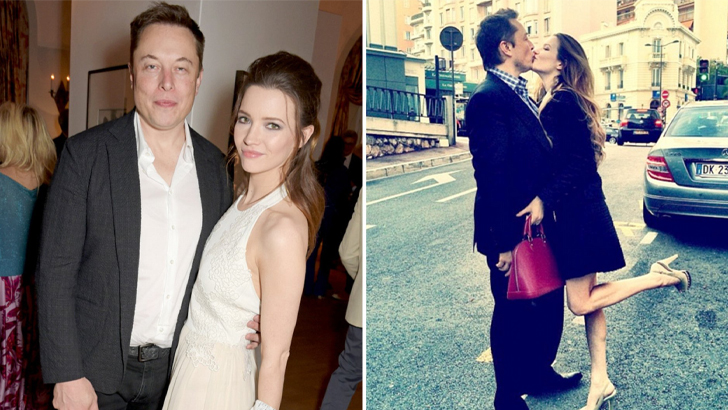

After his divorce from Justine Wilson in 2008, Musk married English actress Talulah Riley in 2010, with an elaborate wedding taking place in the Scottish Dornoch Cathedral. But two years later the two would divorce, only to remarry in 2013, and divorce yet again in 2014 – but that, too, was withdrawn. After an exhausting few years, a second divorce was finalized in 2016.
Musk Foundation

Elon Musk started the Musk Foundation in 2002, and has since made over 350 donations, with about half going to education nonprofits and scientific research, including his alma mater the University of Pennsylvania, Wikimedia and his brother’s nonprofit Big Green. In 2010, they donated a 25-kW solar power system to the South Bay Community Alliance in Coden, Alabama to be used for their hurricane response center. They also donated $250,000 to a solar project in Soma, Japan following a tsunami in 2011.
Mars Promise

In 2011, Musk would proceed to make one of his boldest claims since taking the reins of so many expanding energy and technology companies – he was going to send humans to Mars in the next 10-20 years. While the world marveled at his aspirations, many wondered why we didn’t address concerns on Earth. However, it would propel SpaceX to its next era…
Solar Growth
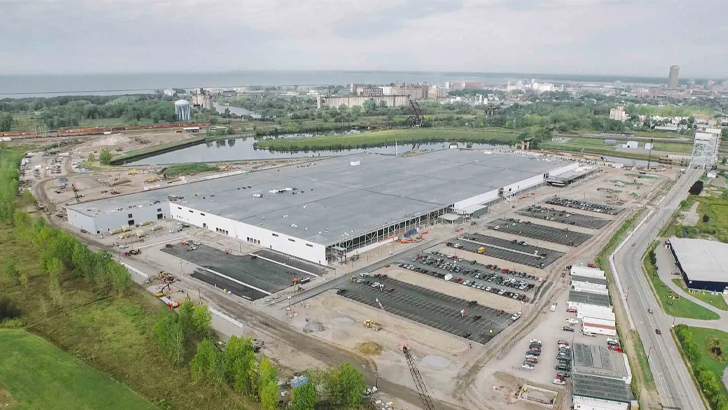

Remember how we told you Elon would reap the benefits of going in on SolarCity with his cousins? Well, the company started working with Tesla to collaborate on creating more powerful batteries for electric vehicles, and this now came after SolarCity elevated to the world’s second-largest solar energy provider. It was then that a whole new production facility was in the works.
Dragon Docks
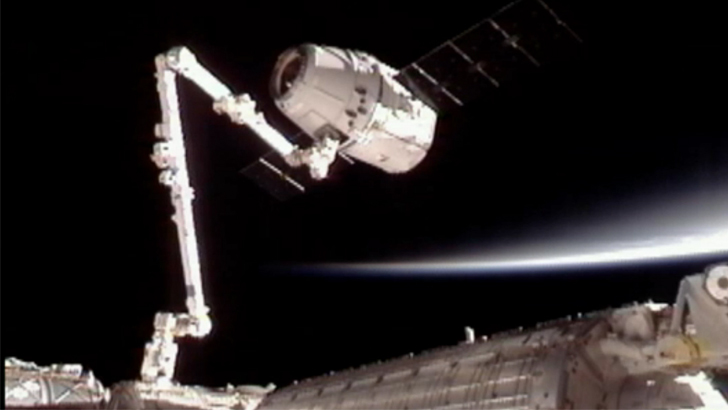

After the painstaking process of trying to acquire rockets, building them independently and watching them fail, Musk finally witnessed his biggest SpaceX achievement to date in 2012. That’s when the Dragon rocket hooked up with the International Space Station for the first time, marking the beginning of the relationship between tangible trade between the two parties.
Open-Sourcing

After the launch of Tesla’s second vehicle, the Model S, Musk announced that Tesla would also be unveiling open-sourcing technologies that would be available to the public. This meant that the patents Tesla may have had to build their electric vehicles would be available to all other car manufacturers, in hopes that they would follow his lead in the electric market and work with them to continue pushing the sector forward.
Simpson’s Cameo
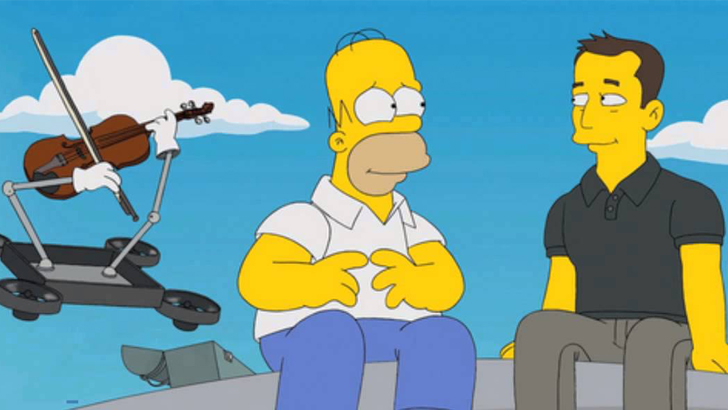

As Elon Musk’s companies continued to flourish and word began to spread of the CEO and engineer’s savvy ability to navigate the business and product side in a way that seemed futuristic. With many curious just who this Musk guy was, his first cameo on national TV came when he was featured on the Simpsons episode, “The Musk Who Fell to Earth.”
The Hyperloop
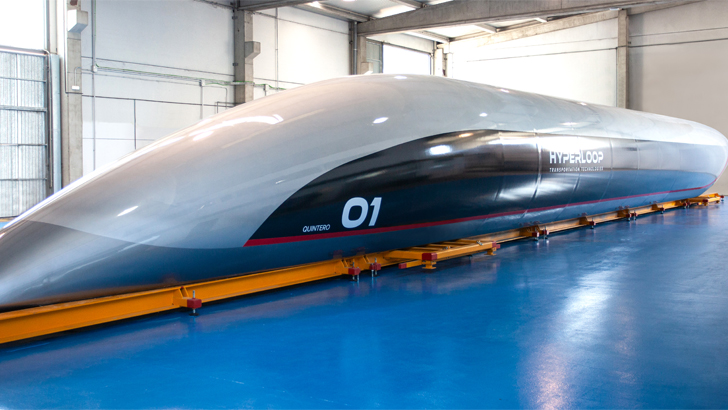

Musk first publicly announced his plans to build a sort of vacuum tube train in 2013, in which he delegated engineers from both Tesla and SpaceX to take part in the project. He would then dub the endeavor the “Hyperloop,” providing a whole model and cost estimate for the idea as well. In 2015, he launched an educational competition challenging students to design their version of the perceived “pod” and actually test them on his mile-long track up until 2017.
Open AI
Musk developed Open AI in 2015 as a nonprofit with the purpose of researching the safety and functional role of AI in society, as well as monitoring and combating threats from large corporations who may abuse such technologies. Ironically, the crafty businessman overlooked his involvement in the field himself, something he’d later have to reconcile with.
Pop Culture Romance
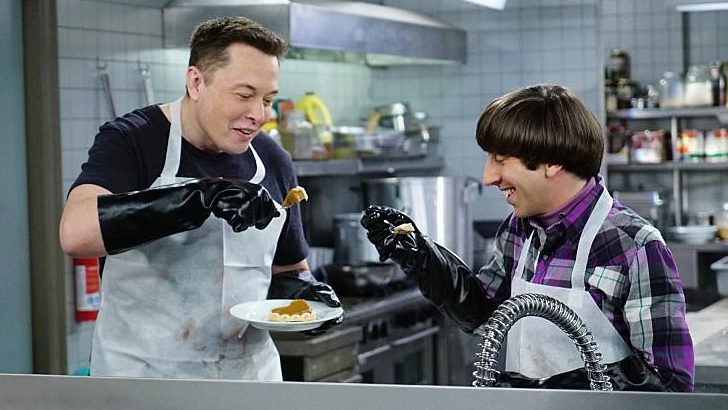

While Musk’s profile continued to rise, and he became more well-known for various things, his personality stock only rose. Not only did he make an appearance on The Big Bang, a popular science-influenced sitcom in which Musk fit perfectly, but he also dated Amber Heard. This obviously has drawn controversy considering the unfolding events in 2022, but he was popular nonetheless.
SolarCity & Tesla

After SolarCity built the largest solar plant in the United States in Buffalo, N.Y., it ended up being triple the size of the next biggest. Originally, Panasonic joined them in the space, but would eventually leave in 2020. In 2016, Musk used Tesla to buy SolarCity for more than $2 billion, with the new plan being that he would merge the companies to form Tesla Energy, with hopes of building better battery energy storage.
Neuralink
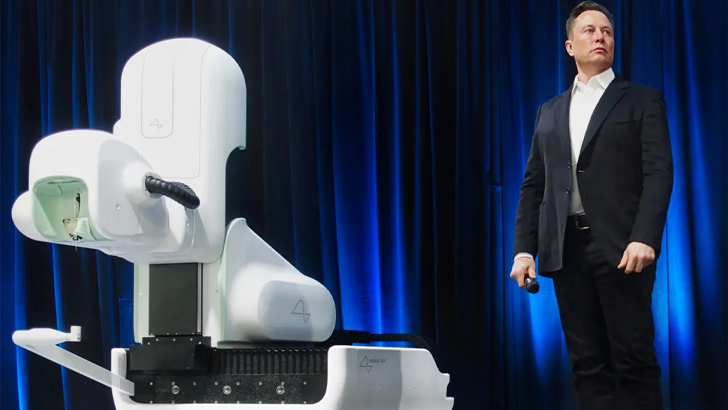

Musk wasn’t done with forming new businesses though, and his next project was Neuralink, a neurotechnology company that would aim to merge the human brain with artificial intelligence, oddly enough by putting a chip in your skull. While he insisted the innovations could lead to better memory or the ability to overcome diseases, medical experts responded skeptically to the potential of such a technology that’s not very understood.
The Boring Company

When it came to Musk’s concept of the Hyperloop, he would need a production crew to help bring his dreams to fruition. Queue The Boring Company, which he founded in order to build these massive tunnels. They built its first testing site in Las Vegas beneath the SpaceX headquarters, completing the 30-ft wide, 50-ft long, 15-ft deep tunnel. It is now a full-fledged infrastructure and tunnel construction company, receiving lots of funding for various projects.
Starlink and SpaceX

After the SpaceX team became successful in their mission to launch rockets independently, the company began developing satellites that would form a constellation in low-Earth orbit, allowing the company to provide internet to numerous companies, with hopes for it to extend worldwide in a decade-long, $10 billion project. The first satellites launched in 2018, with 60 more in 2019.
Colonizing Mars

In 2016, Musk spoke about his mega-project of colonizing Mars in Mexico, explaining the importance and necessity of a “multiplanetary species” that can withstand oncoming climate change that he inevitably accepts will be Earth’s downfall. One of his ideas proposed around this time was using his multiple rockets to eventually become rapid transport between the two planets, also emphasizing the danger and risk involved in such an undertaking.
Musk Leaves OpenAI

As Tesla continued to gain popularity, customers, and had to push innovations themself, Musk was forced to leave OpenAI in 2018 in order to prevent any conflicts that may arise in the future with Tesla’s increasing AI technology. Though serving on the board, the Tesla CEO knew he wouldn’t be able to ethically do both, so naturally he sided with the progressive automotive company.
Dating Grimes
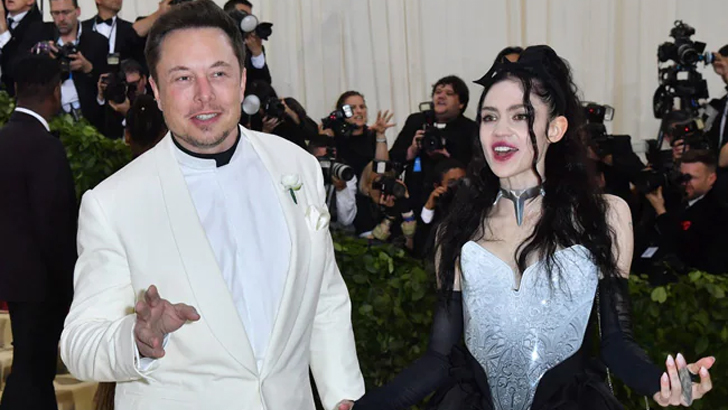 In spring of 2018, reports surfaced that the innovator was dating Canadian musician Grimes, and not long after in 2020, the couple welcomed their first child, who has an infamous name to say the least. They named him X AE A-XII Musk (nicknamed X), and his sister, who was born via surrogate in 2021, is named Exa Dark Sideræl Musk (nicknamed Y). The two reportedly have a fluid relationship, as they are not formally together, but Grimes still calls him “the love of [her] life.”
In spring of 2018, reports surfaced that the innovator was dating Canadian musician Grimes, and not long after in 2020, the couple welcomed their first child, who has an infamous name to say the least. They named him X AE A-XII Musk (nicknamed X), and his sister, who was born via surrogate in 2021, is named Exa Dark Sideræl Musk (nicknamed Y). The two reportedly have a fluid relationship, as they are not formally together, but Grimes still calls him “the love of [her] life.”
Tham Luang Cave
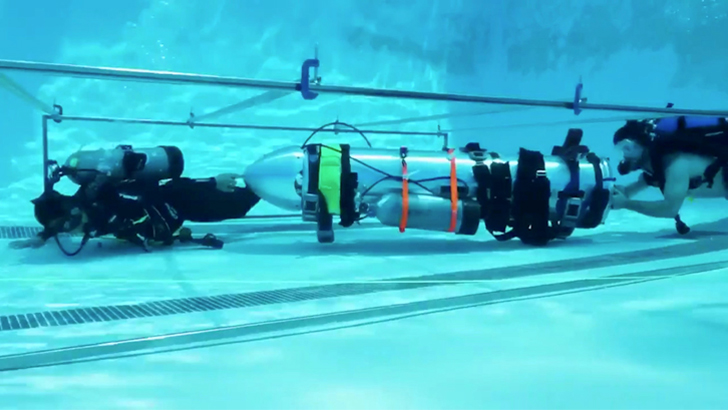

In July of 2018, you may remember the harrowing story of 12 boys who got caught in a flooded cave in Thailand without a way to escape. The lead of an international diving team had requested Musk’s help, so he had engineers at SpaceX and The Boring Company build a mini submarine out of the liquid oxygen transfer tube used in the Falcon 9. But despite getting the vessel on a plane to Thailand within 8 hours, they had fortunately already rescued the children.
SEC Sues Musk
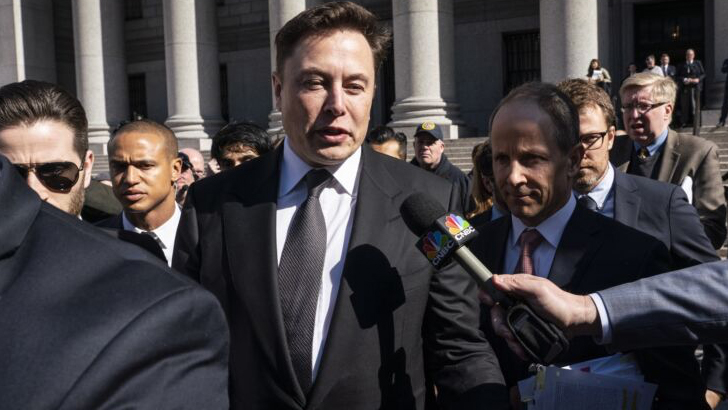

In 2018, the SEC filed a formal lawsuit against Musk for his tweet that Tesla had enough funding to become a privately traded company, stating the claim was untrue and misleading to investors, while also claiming he wasn’t fit to run publicly traded companies. He settled with the SEC just two days later, while both he and Tesla were fined $20 million, forcing Musk to step down as chairman for three years until 2021. He’s had numerous run-ins like this on Twitter, too…
Warning About AI
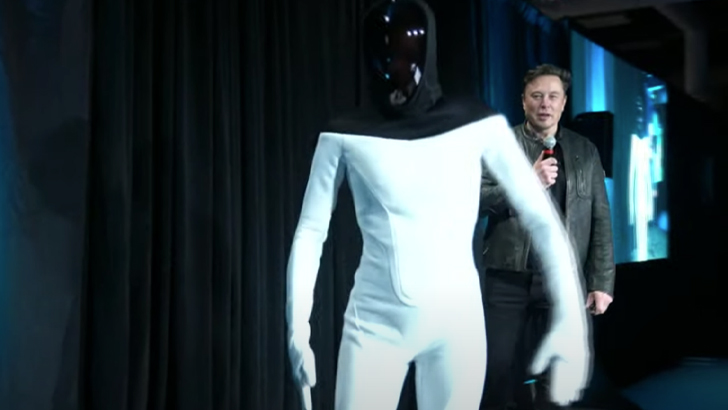

Despite receiving lots of criticisms for his takes on the subject, Elon Musk has been a vocal critic of the dangers of artificial intelligence. He’s claimed the technology poses an existential threat, stating that machine dominance or the concept of “superintelligence” are oncoming threats to the human race, despite various other experts claiming the immediate risks of AI in the present are much greater. For this, he’s often been accused of fear-mongering.
Donations to Flint

Elon Musk and Tesla tweeted a commitment to help the ongoing water crisis in Flint, Michigan, and after being urged further after not hearing results, in 2021 the city announced a new chemical plant, secondary pipeline, and restoration and rehabilitation facilities were constructed with his donation of $480k. The city’s schools are now powered by the 20-million gallon reservoir.
Teslaquila

While Elon Musk decided to explore the world of alcohol, he was forced out of being able to officially call it “Teslaquila,” because Mexico require anything branding itself as “tequila” unless it’s made in Jalisco, one of Mexico’s tequila-producing states. Musk later reworked the name, partnered with a Mexican tequila producer in Jalisco, and came up with a unique bottle design to sell the limited product.
Gigafactories
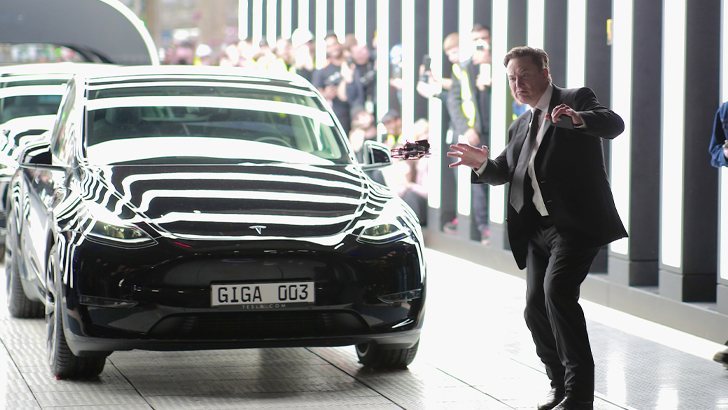

Elon Musk has learned the struggles of production hold-ups first-hand, so once Tesla and SolarCity both grew and merged, he new output would need to be at an all-time high. In come the Gigafactories, which Musk has now built in Nevada, New York, China, Germany, and Texas, in that order. All of them produce or assemble batteries, vehicles, and various components under the framework of Tesla and its lithium-ion technology.
Model Y and Cybertruck

Along with innovative tech within the cars, Musk and Tesla knew that just rising to prominence wouldn’t be enough to convince consumers to go electric, so the next step was designing new vehicles to adapt to various needs of the individual. This led to the unveiling of the Model Y, a crossover-style vehicle, and also the Cybertruck, a futuristically looking electric pickup truck.
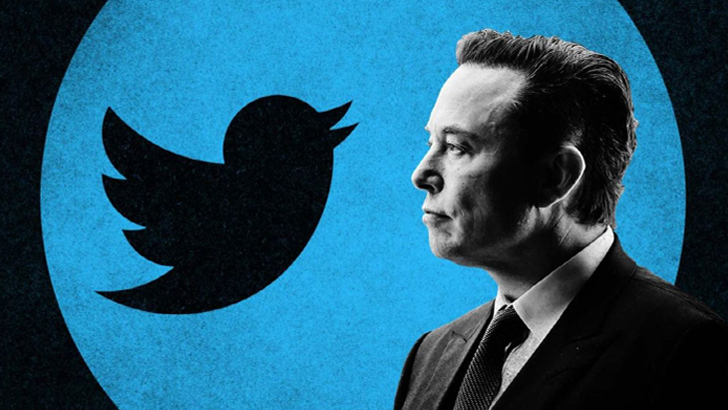

In the most recent business endeavors of Elon Musk, 2022 saw him announcing plans to buy the social media platform Twitter after he already bought increments of increasing amounts of shares since the pandemic, a time when the engineer became much more active on the site. After eclipsing 9% in share, it was announced Musk would buy Twitter for $44 billion, aiming to take the company private once again. The deal is currently still on hold…
Giving Pledge

Musk signed the Giving Pledge in 2012, which is a signed commitment to donating over half his wealth to charitable causes – a gesture largely undertaken by billionaires around the world. And in 2021, Musk earmarked $5.7 million of his own Tesla stocks toward charity in what would become one of the largest charitable donations in philanthropic history.
Transporting Astronauts

SpaceX finally launched its first manned-mission to the International Space Station in 2020, and the Demo-2 became the first independent company to ever send people into orbit and dock at the ISS. In 2023, the company hopes to launch its first dearMoon mission – one which will hope to achieve a full lunar orbit, with passengers aboard.
Helping Ukraine

Upon realizing the ongoing threat of the Russian invasion of Ukraine early in 2022, Elon Musk sent Starlink satellite systems to the country to help combat internet outages happening across the country. Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy praised Musk for his actions, stating that communications that may have been lost were able to be restored. However, he failed to block any Russian access to Starlink.
World’s Richest Man

Elon Musk’s net worth has only increased with the numerous companies he’s founded and invested in, and he slowly but surely has cemented himself as the richest man on Earth, currently sitting with a personal valuation of more than $300 billion – the first to ever surpass this mark. Musk’s wealth is largely tied to Tesla’s success, but the billionaire considers himself “cash poor” as he’s strived to focus less on material, while investing in a multiplanetary species.
More From Financially+
-


Incredible Celebrity Swimming Pools
-


Insanely Awful Park Jobs
-


An Isolated Look Inside North Korea
-


Things to Buy & Avoid at Home Depot
-


Pro Wrestlers Then & Now
-


Here’s What a $500k House Looks Like In Each State
-

The Rarest Diseases Known To Man
-


Historical Photos From World War II
-


Movies Based On True Stories
